-
Optimization of Anti-Leakage Structure and Construction Efficiency for Prefabricated Manholes ——Rapid Construction Technology Based on GB/T 23483 Standard
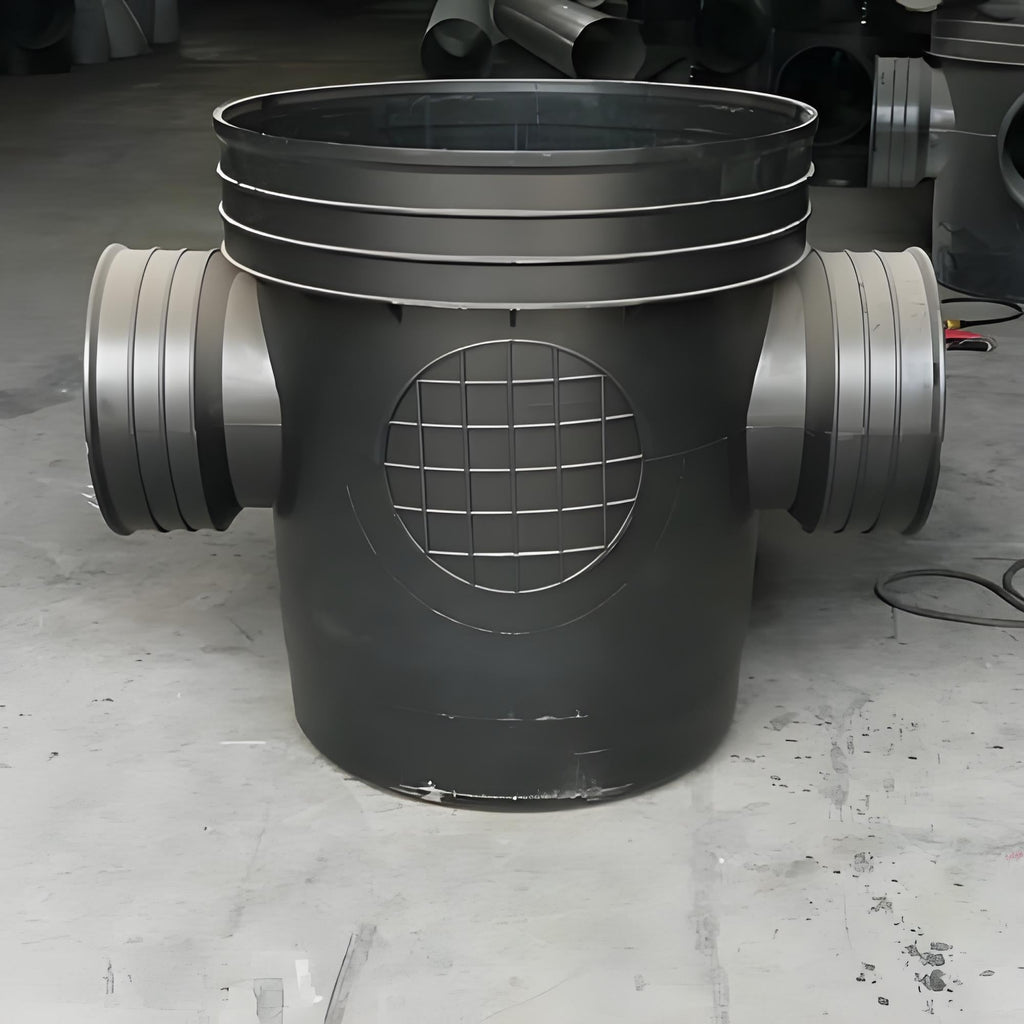
1. Research Background Manholes are critical nodes in municipal pipe networks, responsible for pipe maintenance, water level monitoring, and stormwater collection. Traditional cast-in-place concrete manholes face three major challenges (Figure 1): Long construction 周期: 7-10 days per manhole, accounting for 35% of pipeline project time High leakage rate: 42% of pipeline defects from joint leakage (2024 MOHURD data) Poor durability: 65% crack incidence after 5 years 2. Core Issue: Failure Mechanism of Traditional Manholes 2.1 Failure Mode Analysis Failure Type Cause Typical Scenario Joint Leakage Shrinkage cracks + seal failure Stormwater-sewage intersections Settlement Uneven foundation + low stiffness Soft soil... -
Optimization of compressive performance of cellular structure of PVC-U seven-hole pipe -- Analysis of Engineering Applications Based on GB/T 18477.1 Standard
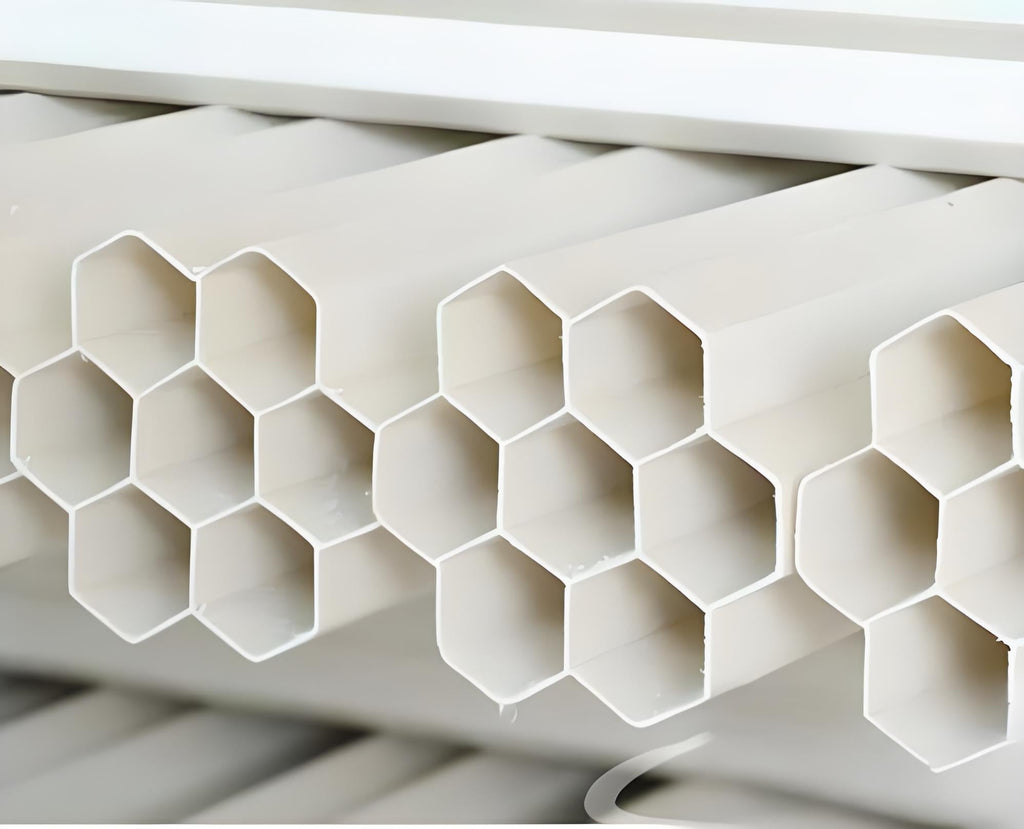
I. Research BackgroundIn the construction of smart cities, PVC-U seven-hole pipe (Figure 1) has become the mainstream choice for small and medium-sized communication pipes because of its **“1 big 6 small” honeycomb structure** (1 Φ50mm main hole + 6 Φ32mm sub-holes). Its space utilization rate is 37% higher than that of single-hole pipe, and its cost is 15%-20% lower than that of nine-hole pipe. However, the deformation of the pipe caused by insufficient compressive resistance of the overburden (accounting for 61% of the failure cases) restricts its in-depth application in municipal engineering.Second, the core problem: cellular... -
Corrosion Resistance Optimization of Steel-Plastic Interface in Steel-Belt Corrugated Pipes ——Design for Buried Drainage Pipes Based on SY/T 4106 Standard
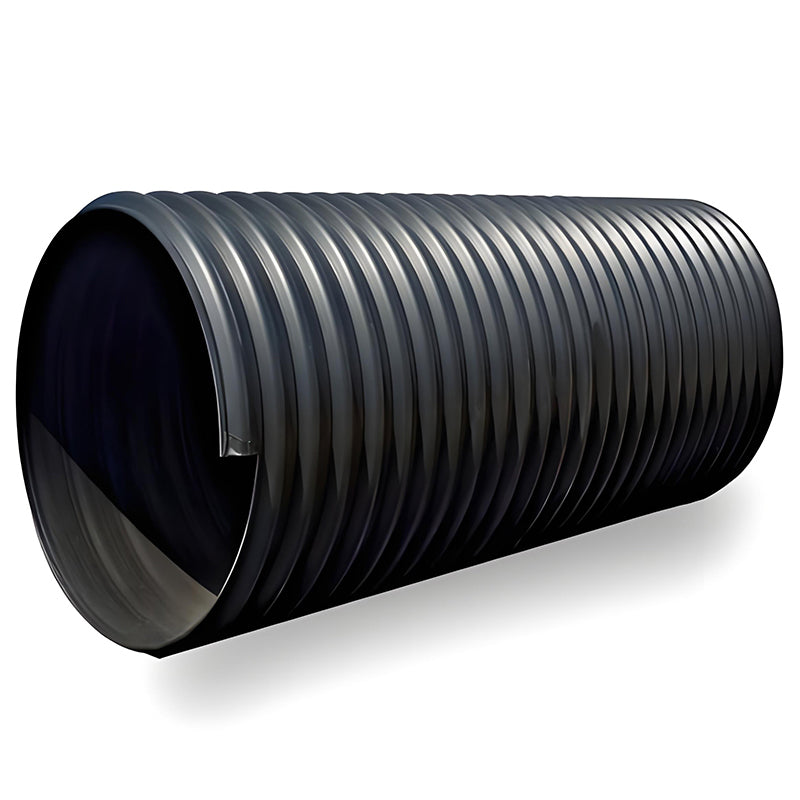
1. Research Background Steel-belt corrugated pipes, with a "steel reinforcement + HDPE composite" structure (Figure 1), occupy 35% of the market for municipal drainage projects with burial depth >4m (2024 China Plastic Pipe Industry Report). While their ring stiffness reaches SN16, steel corrosion causes 41% of failures, especially in coastal saline-alkali soil (Cl⁻ >500mg/L) and industrial wastewater areas (pH <4). 2. Core Issue: Steel-Plastic Interface Failure Mechanism 2.1 Three-Stage Corrosion Process Through salt spray testing (GB/T 10125-2021) and electrochemical analysis, steel corrosion proceeds as: Initial Stage (0-6 months): Localized corrosion at HDPE coating pinholes Medium Stage (6-24 months): Coating delamination due to rust expansion Final Stage (>24 months): Structural collapse with >30% steel...